Intelligent, scalable and 24-hour support provided by businesses is being changed by AI agents. These customer support agents are based on large language models and automation, which can directly respond to customer inquiries and, as well as, process customer inquiries through faster resolution times, better customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. This guide clearly describes the nature of AI agents, their main functionalities, practical application in the industry and how they are transforming smart assistance by 2025 and beyond.
AI agents are self-managing, autonomous, intelligent beings able to reason, adjust, and make decisions instantaneously.
“35% of companies report broad adoption of AI agents, while 17% indicate that AI agents are now fully integrated across nearly all workflows and functions.”
Whether it is the customer service revolution to simplification of complex tasks, these agents are no longer a far stretched dream. In the future these agents are already predicted to transform the industries and change what is considered productive. This authoritative book takes an in-depth look at the nature of AI agents, their functionality, their use in the real world, and what we should expect in the future so that you are no longer at a disadvantage when it comes to exploiting this technology disruptor.
What Are AI Agents?

AI agents are computer programs fuelled by artificial intelligence and designed to carry out tasks autonomously, make decisions or correspond with a user/system, to accomplish a given objective.
Contrary to more traditional approaches to chatbots that use pre-written responses (i.e., continue to respond in scripted ways), or robotic process automation (RPA), whose behavior is governed by strict rules, AI agents apply machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and large language models (LLM) to dynamically learn new information.
They are aware of the surroundings, process complicated situations, and have the ability to autonomously respond to situations, thereby making them an interpolatable business tool.
Namely, although a chatbot may have a hard time dealing with a sophisticated customer request, an AI agent will be able to make an intent analysis, consult knowledge base, and make a specific response, or even transfer the issue to a human agent, having provided all the context. In fact, the MarketsandMarkets report predicts that the AI agents market will also rise in value, reaching a mark of 47.1 billion dollars by 2030, which shows their huge potential.
Key Components of AI Agents
AI agents are built on several core components that enable their autonomy and intelligence:
1. Perception: Agents collect data from their environment, such as customer queries, database records, or IoT sensor inputs.
2. Reasoning: Agents analyze, interpret, and make decisions using machine learning models and large language models.
3. Action: Agents perform actions, to answer questions, to automate processes, or to cause updates to the system.
4. Memory: A long-term memory means that the agent stores user preferences, previous interactions or results of a task and uses this knowledge to perform better in future.
5. Learning: The agents can also gradually perfect behavior based on feedback loop and reinforcement learning.
These are the aspects that make AI agents different to traditional automation allowing it to react to dynamic and unpredictable environments.
How AI Agents Work?
AI agents operate in a continuous loop of sensing, analyzing, and acting.
- Inputs: Provides access to the query as a text, voice or other method.
- Interpret: Through NLP, is able to interpret intent and sentiment with a knowledge base and backend systems being cross-referenced.
- Makes Decisions: Decides to take an action, escalate to a human or activate an automated work flow.
- Executes: Demonstrates an action, response, or execution of task, e.g. an upgrade of a CRM system.
- Learns: Memorizes the conversation to allow better responses in the future.
This is the work provided by innovative AI, such as LLMs, like those of ChatGPT. It allows working with natural language; and APIs or databases, through which real-time guidance will be available.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents are generally classified into five main types: simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents. Such agents vary in the way they perceive the environment, adjust to this or that change, and decision-making.
Let us sort out these types one by one:
1. Simple Reflex Agents: These are the most simple class, which purely exists as per the input stimulus (current perception) according to pre-decided rules and do not take past experiences or future outcomes into account when making decisions.
An example is a smart thermostat that switches the heater on or off depending on the room’s current temperature.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents: These agents depend on an internalized model of the environment, and thus they are able to keep track of the current state and its time-dependent transition. This knowledge will assist them in making better and contextual decisions.
For example, a robot that bases its movements to follow an existing map of the immediate area, although it is outdated to some extent.
3. Goal-Based Agents: These are agents that perform an action in an attempt to reach a certain goal.
Example: An AI that plays chess and considers the state of the game and makes some decisions, winning the game through the checkmate.
4. Utility-Based Agents: These agents go beyond simply achieving a goal, they also evaluate the desirability or utility of possible outcomes and choose the action that maximizes overall benefit or satisfaction.
Example: A portfolio management agent which looks at stocks balancing risk and reward to give maximum returns.
5. Learning Agents: These kinds of agents are able to learn on the basis of past things and enhance their performance requirements in the future.
Example: A spam filter that would learn to distinguish between spam and non-spam mails depending on the statements of the user.
6. Hierarchical Agents: Such agents structure their decision making process in terms of levels of abstraction and the higher level agent directs the lower level agent in the process.
7. Multi-Agent Systems: These are systems of multiple AI agents which interact, and perhaps co-operate to reach a shared goal.
Real-World Examples of AI Agents
AI agents are already generating tangible results across a wide range of industries. Here are some compelling examples:
1. TaskRabbit’s Customer Service Revolution
An online marketplace, TaskRabbit, specializing in matching freelancers with local demand had to deal with its customer service tickets increasing by 60 percent to 158,000 per month. What TaskRabbit did was automate answers to frequently asked questions by using Zendesk AI agents.
Resultantly, it moved to a higher customer satisfaction level and grew support without hiring more people. These agents could identify the intent of the customers, tap into the knowledge banks of the business and fix problems without any human intervention to reach a level of 30 percent automation.
2. Domo’s Marketing Workflow Automation
A marketing team using Domo’s Agent Catalyst built an AI agent to automate follow-ups for weekly strategy meetings. Previously, team members spent hours transcribing notes and emailing summaries.
The agent now transcribes, identifies action items, and sends personalized emails, saving hours weekly and improving accountability. This no-code solution highlights how AI agents democratize automation for non-technical users.
3. Gumloop’s Revenue Surge
Gumloop, a no-code AI automation platform, helped a business generate 65% more meetings year-over-year and win 207% more revenue by deploying AI agents to automate outreach and scheduling. The intuitive UI allowed non-developers to create workflows, showcasing the accessibility of AI agents.
4. Zapier’s Lead Generation
Zapier’s AI agents automated lead generation, producing over 2,000 leads in a single month. Integrated with 7,000+ apps, these agents handled tasks like data enrichment and CRM updates, allowing teams to focus on strategic priorities.
Benefits of AI Agents
The following are the revolutionary advantages of AI agents to businesses, staff and customers:
1. Improved Productivity
Repetitive tasks often lengthen the process required to accomplish an objective with the involvement of a human workforce. AI agents can simplify performing high-value tasks for the teams by automating them. To give an example, Zendesk AI agents can reach a cumulative 80 percent automation level of customer requests, saving on manual work.
2. 24/7 Support
There is round the clock support by the use of Agents, so customers get immediate help no matter the time zone.
3. Personalization
The agents access customer data and provide personalized answers to them by connecting with other backend systems that enhance customer satisfaction.
4. Cost of Operating
Automation reduces the amount of money spent in the operations. According to a recent survey by LangChain, 51% of companies are using AI agents to make data-backed decisions and reduce resource waste.
5. Scalability
Agents handle surging demand without additional staffing, as seen in TaskRabbit’s case.
6. Actionable Insights
Agents analyze interactions to identify trends, enabling proactive improvements.
7. Multi-Channel Consistency
AI agents have the ability to work on multiple channels such as email, social media or voice to provide consistent and coherent service.
8. Continuous Learning and Self-Proficiency
Most AI agents are expected to learn from user’s conversations or contextual knowledge and understanding.
9. Localization and Multilingual Support
Localization and multilingual support becomes a breeze as AI agents are modeled to converse in different languages; therefore, businesses with multilingual customers no longer have to employ multilingual staff just to maintain them.
10. Data Privacy and Compliance Monitoring
The contemporary AI agents can be programmed to comply with the regulations (such as GDPR or HIPAA). It guarantees that customer information is handled safely and in line with the laws.
Challenges and Limitations
Although AI agents are powerful, there are challenges that should be overcome by the businesses, such as:
- The lack of Empathy: Agents might not be able to deal with emotionally sensitive situations and might need human escalation.
- Complex Queries: Complex queries that are unseen during training that are subtle or unique may produce an error.
- Privacy: The processing of sensitive data requires strong security proofs such as encryption and GDPR to be adhered to.
- Over-dependence: This danger is inherent in too heavy use of agents as it will tend to make human skills obsolete.
- Hallucination Possibility: There is a risk of poor answers that LLMs can produce, which requires monitoring and guard rails.
End to End Steps to Create AI Agents
Developing an AI agent has never been easier because of no-code/low-code software tools such as Domo, Gumloop, and Zapier. Here’s our tried-and-tested step-by-step guide to building an AI agent for greater clarity and ease of use.
1. Define Objectives: Define Issues, like automation of customer support or the analysis of the data. Prepare defined objectives, such as cutting down on response time by 50 percent.
2. Select a platform: Select a tool such as Domo no-code workflows or n8n developer. It should have compatibility with your systems.
3. Design Workflow: Diagram the work flow of an agent including queries on a database or sending emails. No-code platforms make use of visual editors for building workflows and functionalities.
4. Setup Data Sources: Link the agent to knowledge bases, CRMs or APIs to have the ability to access real time data.
5. Fine-Tune the Model: Refine the model using domain-specific data to enhance its accuracy and performance.
6. Test and Iterate: Test and repeat to find out mistakes. Follow productivity measures such as precision and customer satisfaction.
7. Deploy and Monitor: Deploy the agent and utilize analytics to monitor the performance, and polish it accordingly.
The Future of AI Agents

The prospects of AI agents will face towards a promising future and it will have greater effects:
- Emotional Intelligence: The agents will be more likely to recognize and deal with human emotions to improve the mental support or customer experience.
- Multimodal Capabilities: The text, voice, images and video will all be integrated so as to facilitate richer interaction, including visual troubleshooting.
- IoT Integration: Smart devices will be under the control of agents, optimizing homes, cities and offices.
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: Groups of agents will solve complex tasks so that one of them may be specialized in data analysis or the process of communication.
- Ethical Design: Responsible AI will lay emphasis on being fair, minimizing the biases, and being compliant.
- Generative AI: CloudMoyo anticipates that 80 percent of enterprises will have deployed generative AI-enabled applications inclusive of agentic AI by the year 2026.
How to Implement AI Agents in Your Business?
The following best practices can be employed to have the best chances of adopting AI agents:
1. Start Small: To get started, do one use case, such as automating FAQs, test and learn.
2. Know Security: Encrypt data and apply restrictions to access.
3. Train Staff: Teams should be trained on how to work with agents to the greatest extent.
4. Measure Performance: Display analytics to help monitor performance and resolve problems such as hallucinations.
5. Gradually Upscale: To grow into new use cases by building confidence.
AI Agents vs. Traditional Automation
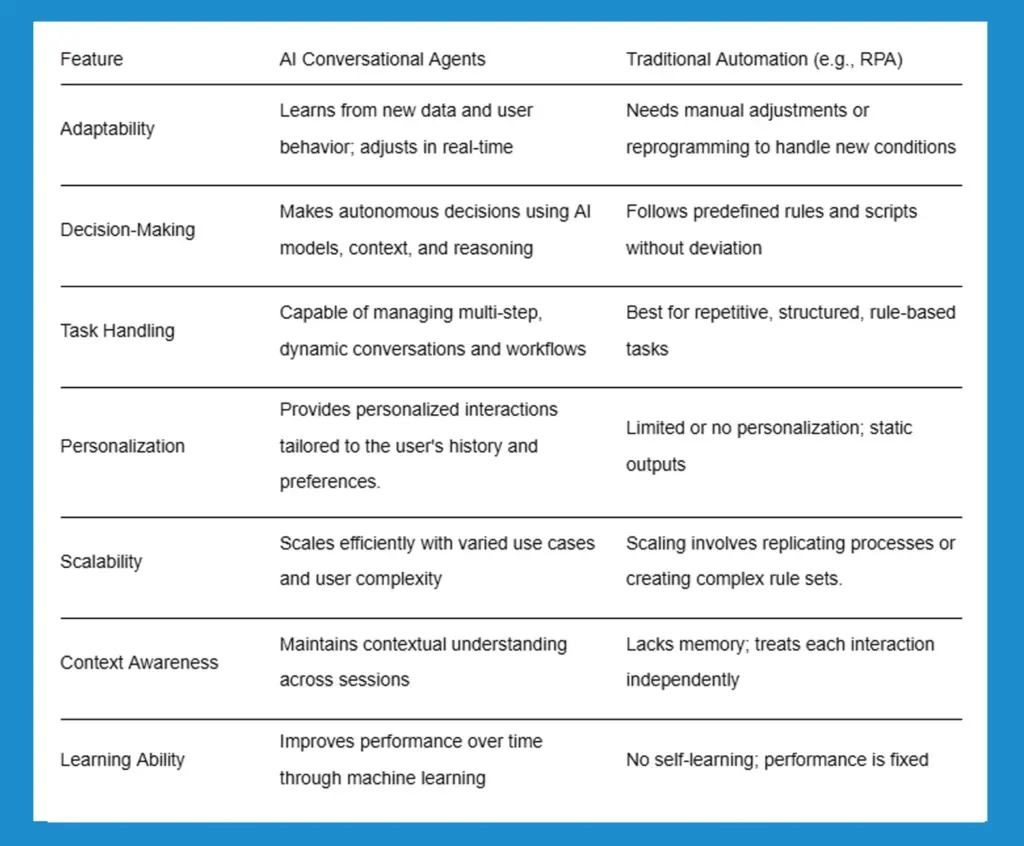
AI agents differ significantly from traditional automation:
Dealing with heavy work burden or slow response duration?
When your customers have to spend too much time without assistance, or when your team is overloaded, it is time to re-engineer the process of work. At BrainX, we are experts in creating AI agents that directly address these business challenges.
Our AI development services help you automate repetitive tasks, provide quick responses, and work 24/7 without having to burn out. We provide assistance tailored to your business requirements, so they grow as you grow, and free up your team to do what really counts.
Together we can eliminate the bottlenecks.
Talk to BrainX about building an AI agent that actually moves the needle!
FAQs
1. What is an AI agent in customer support?
A software-based assistant, an AI agent applies artificial intelligence (particularly NLP and machine learning) to tasks such as question answering, ticket routing, problem solving and personal assistance - commonly real time and at scale.
2. What is the efficiency of AI agents in terms of support?
Artificial intelligence agents minimize the amount of time taken to respond, respond to monotonous questions, and they work 24/7 without fatigue. This increases the response rates in the first-response and also leaves human teams to high complexity tasks.
3. Are chatbots equivalent to AI support agents?
Not exactly. Although the two can communicate with the users, AI agents are more developed. They apply contextual knowledge, recollection and autonomous choice- usually combined with CRMs, databases and APIs.
4. What industries are the most efficient with the use of AI support agents?
The industries that have benefited most include eCommerce, SaaS, healthcare, real estate, and logistics- anywhere customer interaction, ticketing or process automation is required.
5. Are AI agents able to substitute human support teams?
No. AI agents do not substitute human agents, but complete them. They are dealing with routine tasks, pushing the complex ones to humans, and making sure that costs are saved and user experiences are improved.